It’s finally time for our next Experts’ Talk article and we’re excited to share unique trends, insights, and perspectives from the cybersecurity world with you. This month we are joined by the Information Security Expert and certified Cybersecurity Consultant Steliyan Petkov with whom we will be exploring the topic of why data encryption is important and how it can help you minimize cybersecurity risks for your organization. Steliyan Petkov is a well-known expert in the field of Cybersecurity who has valuable experience gained across the highly regulated FinTech and Pharmaceuticals Industries. He focuses on assessing and evaluating risk from which Information Security Strategies can be both developed and enhanced. Steliyan Petkov’s expertise is further supported by his CISM, CISSP, and CDPSE Certifications.
What does it mean to encrypt your data?
So let’s not waste a minute and get started by defining what exactly does data encryption mean. Encryption is the process through which cryptographers transform data into code intending to protect it from unauthorized access. Usually, the sensitive data is scrambled and ordered in a practically unreadable way, and the information that it gives out does not make any sense. This unreadable text is referred to as ciphertext. To read the information users have to decrypt the ciphertext so that it transforms to its initial state of plaintext.
“Encrypting data is not a new concept, it has been around for centuries. One of the oldest and most widely-known encryption techniques is the so-called Caesar’s cipher, named after the infamous Julius Caesar who used it to protect military messages. To encrypt a message using Caesar’s cipher you would need to replace each letter from the plaintext with a letter from the alphabet that is positioned a certain number of spaces before the letter that you need to replace. We refer to this number as the key because if the user knows what the number is, they can easily decipher the message. It sounds complicated, but it is actually pretty simple. So, for example, if you select the number 4 to be your key, then the letter A in the plaintext will be substituted by the letter W in the ciphertext, while the letter D will be switched for an A and so on. This method of encryption is called a substitution cipher, and while it was useful some decades ago, now we need to use more complicated methods of encryption.”, shares Steliyan Petkov.

So, for example, if you wanted to encrypt the word “CYBERSECURITY” by using Caesar’s cipher with a key of 3, you would end up with the following ciphertext: “ZVYBOPEZROFQV”. Another historical use of substitution cipher during WW2 is when the German Enigma machine was invented to help military officials send and receive secret information in the form of substitution cipher.
The encryption of data is still widely used today and it is arguably one of the essential cybersecurity practices. In fact, organizations and companies are often obligated to encrypt any sensitive data that they store or send via diverse communication platforms on the Internet. As Steliyan Petkov puts it, encryption could not only protect organizations from being hacked, but in case of an existing cyberattack, encryption could also make the difference between a massive breach of personal data and a compromising of unreadable ciphertext.
“If you don’t encrypt the sensitive data your company handles, you are exposing your business to enormous risk. And I’m not only talking about the risk of a data breach, but also the risk of non-compliance with certain regulations and industry requirements. Consequently, if you’re not compliant, you may be faced with fines and reputational damages.”, adds Petkov.
Before we share which regulations require businesses to encrypt their data, however, we’ll first explore the different types of encryption used today.
Types of Encryption
There are two main types of encryption – Symmetric and Asymmetric (also known as public-key encryption). The differences between them lie in the speed of the process, the number of keys needed to encrypt and decrypt data, the length of the keys, as well as the means through which the keys are shared with other parties (key management).
-
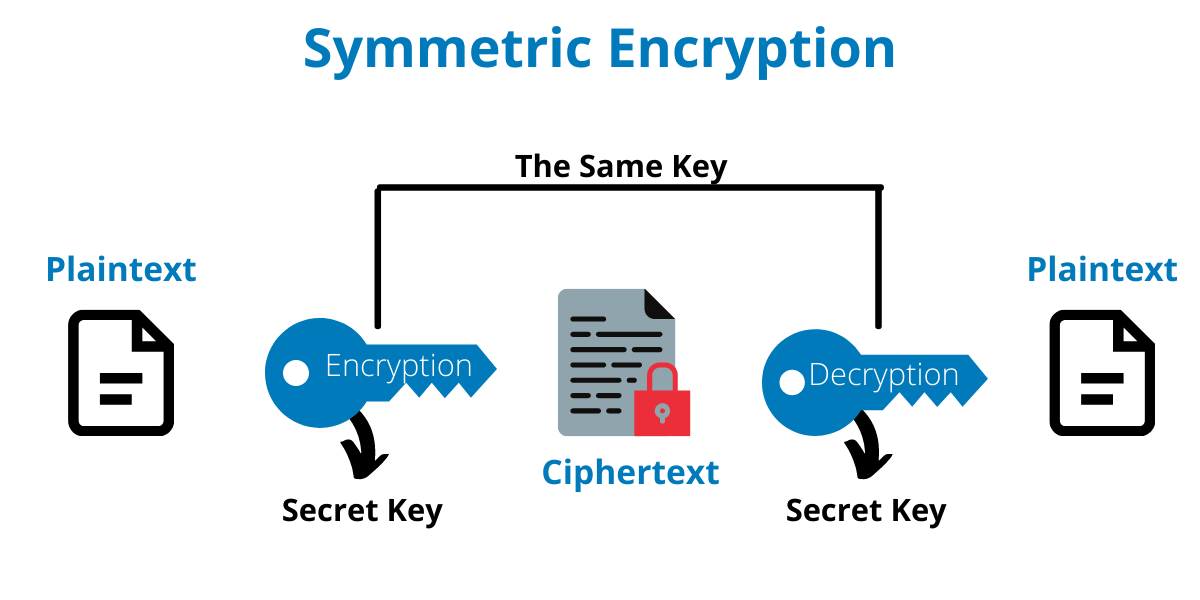
Symmetric
This type of encryption uses one key for both processes – encryption and decryption. So, for example, if you want to send a secret message to John, you need to provide him with the encryption key, so that he can decrypt your message. Therefore, the risks associated with symmetric encryption are higher. As Steliyan Petkov explains it:
“When only one key is used for encryption and decryption, both parties that participate in the communication need to know what that key is. Thus, the key needs to be exchanged and if this process is not done safely, the key could fall in the wrong hands. For example, you cannot simply send the key to the other party via email without it being encrypted itself. There are specific procedures that need to be followed when it comes to key management.”
-
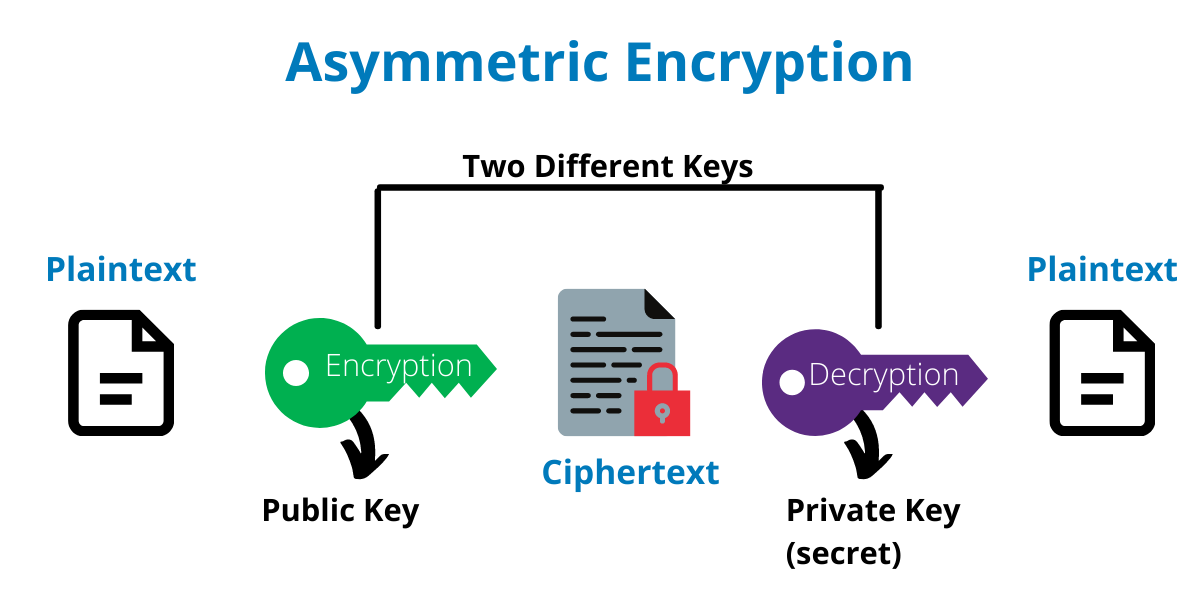
Asymmetric
With asymmetric encryption, there are two keys involved – one for encrypting the message (a public key) and one used to decrypt it (a private key). When this method is used, the sender encrypts the message with the public key and the receiver decrypts it with his/her private key.
“The public key is available to anyone, hence the name. On the other hand, the private key is only known by the person receiving the message. Therefore, asymmetrically encrypted messages are less likely to be compromised by cybercriminals.”, clarifies Petkov.
Because symmetric encryption is not as complicated as asymmetric, it is also a much faster process. Furthermore, the recommended length of the keys associated with both types of encryption is different. While in our example with Caesar’s cipher we only used a key containing one number (3), in reality, encryption keys consist of hundreds or thousands of numbers.
“The encryption keys are essentially strings of symbols (digits, letters and some special characters) with different lengths. They could consist of 128, 192, or 256 numbers (professionals usually refer to those numbers as bits) and could even contain more than 2048 bits. At the time of writing, the recommended symmetric key length is 128 bits and higher, while the length for asymmetric keys is 2048 bits and higher.”, shares Steliyan Petkov.
Why should you encrypt your sensitive data?
Encrypting your data is crucial for your organization’s cybersecurity regardless of the industry your business operates in. Steliyan Petkov shares that many industry regulations require companies to encrypt their sensitive data:
“Whether your business operates in the financial, healthcare, or any other sector, it’s strongly advisable, and in some cases compulsory, to encrypt the sensitive data you handle. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), for example, requires organizations to protect patients’ data via encryption or an equivalent alternative. Additionally, businesses can avoid hefty data breach fines from the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) if the breached data cannot be accessed without a decryption key. Not to mention that the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), as well as the Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) require organizations to encrypt sensitive data and anyone who fails to do so will be faced with expensive penalties.”
According to The Global Encryption Trends Study 2021 by Entrust, the data types that were routinely encrypted in 2020 were payment-related data (55%), financial records (55%), intellectual property (48%), employee data (48%), customer information (42%), healthcare information (26%), and non-financial business information (25%). Furthermore, according to the same study, the top four reasons for encryption in 2020 were:
- Protecting customer information – 54%
- Protecting information against specific, defined threats – 50%
- Protecting intellectual property – 49%
- Complying with privacy or data security regulations and requirements – 45%
It’s best if you outsource the task of encrypting your data to a professional cybersecurity team with the needed experience and expertise. 3Cyber-Sec’s team can protect your organization from cyber threats. As a boutique cybersecurity consultancy, we are passionate about providing tailored solutions to each of our clients and we’re always ready for new challenges. Contact us for a free consultation now.
Did you enjoy our article? For more expert advice, read our last month’s talk, when we were joined by 3Cyber-Sec’s Business Development Manager and certified Cybersecurity Consultant Todor Kunev. Together with him, we discussed the dangers phishing attacks propose for businesses and individuals.

